Curious about thyroid scans? Learn how they help doctors check your thyroid and body functions. Discover how this test can give you answers you need!
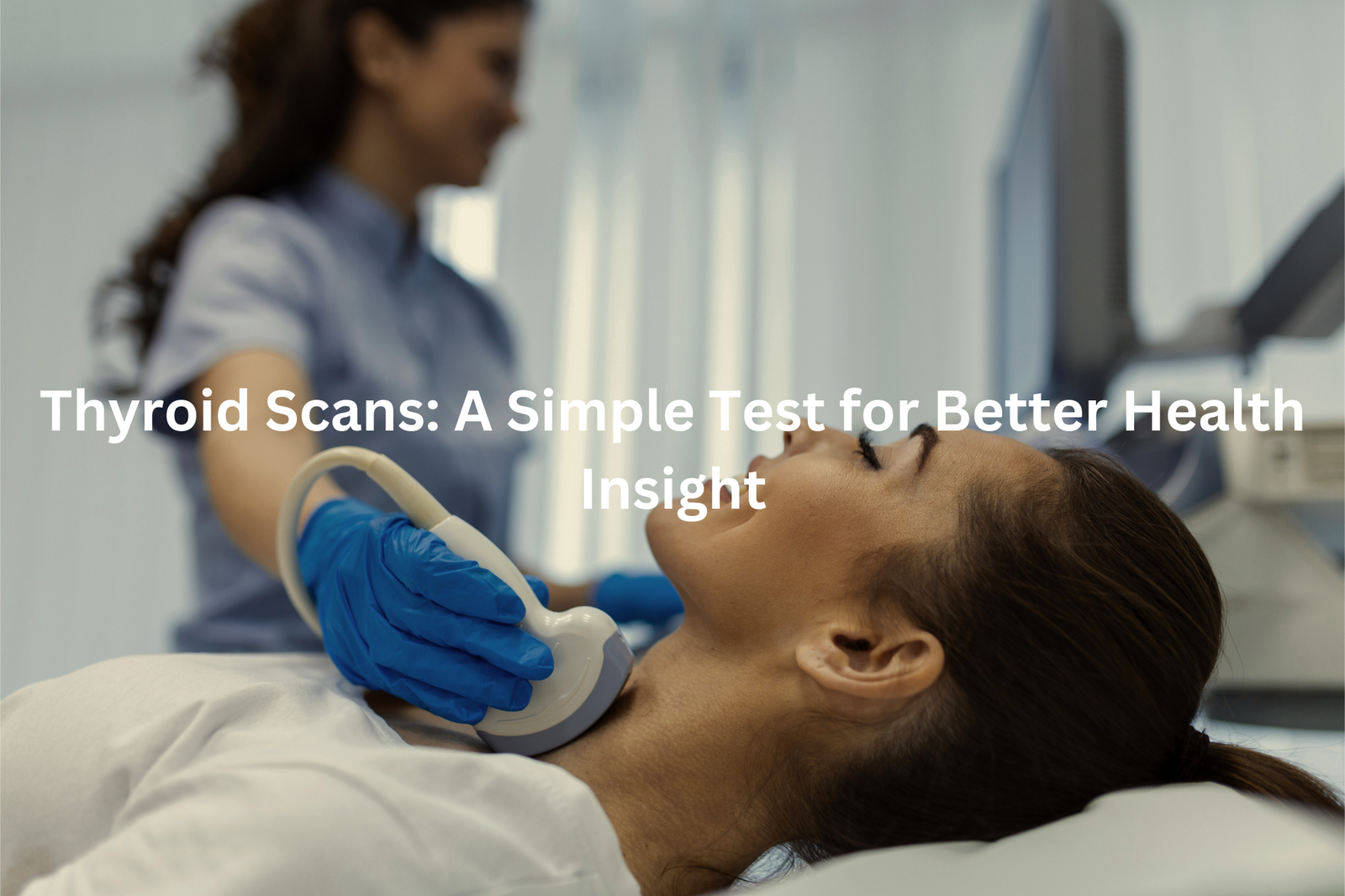
Thyroid scans provide detailed images of this butterfly-shaped gland that sits at the front of the neck. During the scan, a patient receives a small dose of radioactive material (typically iodine-123 or technetium-99m), which helps doctors see how the thyroid functions.
The scan takes about 30 minutes, showing areas that are working too much or too little. A special gamma camera captures these images while the patient lies still on a table. The procedure doesn’t hurt, though patients need to avoid certain foods and medicines beforehand. Doctors use these scans to check for lumps, swelling, or other thyroid problems that blood tests might miss.
Key Takeaway
- Thyroid scans help check the thyroid gland’s health and function.
- They use a small amount of radioactive material, which is safe.
- These scans can help doctors diagnose thyroid problems early.
What is a Thyroid Scan?
A thyroid scan at Royal North Shore Hospital in Sydney shows how a small gland controls major body functions. This butterfly-shaped organ, roughly the size of two thumbs together, sits in the front of the neck.
The scanning process starts with a radioactive iodine pill (about 0.5 millicuries). After 4 hours, the iodine travels through the body to reach the thyroid. During the 30-minute scan, patients lie still while a gamma camera takes detailed pictures.
Steps for a thyroid scan(1):
- Taking the radioactive tracer pill
- Waiting period of 4 hours
- Lying on the scanning table
- Gamma camera imaging (30 minutes)
The radiation exposure from this test measures less than a Sydney to Perth flight. Medical staff consider it one of the safest diagnostic procedures available. Patients should tell their doctors about pregnancy or breastfeeding before the scan, as these conditions might affect the procedure’s safety.
Why Do People Get Thyroid Scans?
A thyroid scan at Australian hospitals takes just 30 minutes – quicker than most TV shows. The process starts when a patient receives a tiny dose of radioactive material (technetium-99m) through an injection(2). A specialized gamma camera captures images while the patient lies still on a table.
The scan helps doctors find:
- Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
- Unusual growths or lumps
- Problems with hormone production
Medicare covers most thyroid scans at major facilities like Royal North Shore Hospital and I-MED Radiology Network across Australia. The procedure doesn’t hurt, and there’s no recovery time needed.
Preparation guidelines:
- No food for 4 hours before the scan
- Stop thyroid medication on scan day (if applicable)
- Wear comfortable clothes
- Remove metal jewelry
The nuclear medicine staff monitors everything closely, making sure the radiation exposure stays at safe levels. Patients can go about their normal day right after the scan’s done.
What Happens During a Thyroid Scan?

A thyroid scan at major hospitals needs careful preparation. The process starts with dietary changes before the procedure.
Patients must avoid iodine-rich foods, including:
- All seafood and seaweed
- Iodized salt
- Dairy products
- Eggs
The procedure begins with a small dose of radioactive iodine (around 0.5 milliliters in liquid form). Medical staff monitor the absorption process, which takes 2-4 hours. During this waiting period, patients stay in a designated area.
The scanning process uses a gamma camera and takes approximately 30 minutes. The camera captures detailed images of the thyroid gland while the patient lies still on the examination table.
For best results, patients should:
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing
- Avoid metal accessories
- Follow all dietary guidelines
- Arrive 15 minutes early
- Bring reading materials for the waiting period
The entire procedure typically finishes within 5 hours, including preparation and scanning time.
What Can a Thyroid Scan Show?
Sources: Dr. Paulien Moyaert.
Thyroid scans at major medical centers work as diagnostic tools to spot issues in this small but mighty gland. The process takes roughly 30 minutes (not counting the usual 20-minute paperwork), using a gamma camera that circles the neck area.
These scans highlight three key features:
- Active areas (hot spots) that absorb iodine quickly
- Inactive regions (cold spots) with minimal iodine uptake
- Abnormal growths or nodules
The imaging machine captures multiple views of the thyroid, creating detailed pictures that look similar to thermal maps. Medical staff then analyze these images on computer screens to check for potential problems.
Preparation guidelines:
- Choose metal-free, comfortable clothing
- Skip seafood for 3-4 days before the scan
- Allow about an hour for the entire procedure
Most patients find the scan straightforward, though staying still during imaging requires some patience. The procedure needs no recovery time, and patients can resume normal activities right after.
Safety and Side Effects

Thyroid scans at Australian hospitals use such a small amount of radiation, it’s like taking a flight from Sydney to Perth. The dose, about 0.035 millisieverts, falls well below safety limits set by ARPANSA (Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency).
Nuclear medicine departments across Australia follow strict protocols for these diagnostic tests. The process is quick, straightforward, and monitored by trained professionals who make sure everything runs smoothly.
Key safety points about thyroid scans:
- Radiation exposure equals one domestic flight
- Certified technicians handle all procedures
- Tests last about 30 minutes
- No lasting side effects
- Results available within 24-48 hours
Patients who feel worried can ask their GP about the procedure. Most medical centers provide information sheets explaining the process step by step. The scan helps doctors check thyroid function and spot potential issues early, making it a valuable diagnostic tool in modern medicine.
Benefits of Getting a Thyroid Scan
Thyroid scans at Australian hospitals take about 30 minutes, with the actual scanning process lasting 15 minutes (using gamma cameras that detect radioactive material). These non-invasive medical tests help doctors spot potential thyroid problems before they become serious.
The scanning procedure maps out the butterfly-shaped thyroid gland, which sits in the front of the neck and controls many bodily functions. During the scan, patients lie still while special cameras capture detailed images of their thyroid.
Key benefits of thyroid scans(3):
• No surgical procedures needed
• Quick process, usually under an hour
• Provides detailed images for accurate diagnosis
Common signs that might need a thyroid scan include unexplained fatigue, irregular weight changes, or neck discomfort. Medicare covers most thyroid scan costs in Australia, making them accessible at major hospitals like Royal North Shore in Sydney. Patients should discuss any thyroid concerns with their GP, who can refer them for appropriate testing.
FAQ
What is a CT scan and how does it help diagnose thyroid problems?
A CT (computed tomography) scan is a type of medical imaging that can help identify thyroid issues. It uses X-rays to create detailed 3D images of the thyroid gland, allowing doctors to check for thyroid nodules, cancer, or other abnormalities. CT scans are often used alongside other tests like blood work to get a comprehensive understanding of your thyroid health.
How do thyroid hormone levels (TSH, free T4, free T3) impact my health?
Your thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate your metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. An imbalance in thyroid hormone levels (low TSH, high/low free T4, high/low free T3) can cause problems like weight changes, fatigue, or irregular heartbeat. Regular blood tests to measure these levels help your doctor monitor your thyroid function and adjust treatment if needed.
What is the role of the TSH test in diagnosing thyroid conditions?
The TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) test measures the amount of TSH in your blood. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland and signals the thyroid to make more or less hormones. High or low TSH levels can indicate an underactive or overactive thyroid, helping your doctor diagnose conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
How do I prepare for a thyroid blood test or scan?
For most thyroid blood tests and imaging scans, you’ll simply need to provide a blood sample. No special preparation is usually required, but your doctor may ask you to fast beforehand or stop certain medications temporarily. Be sure to discuss any concerns about radiation exposure from tests like iodine uptake scans with your healthcare provider.
When should I get my thyroid checked, and what do the results mean?
Your doctor may recommend thyroid testing if you have symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, or mood swings. They’ll likely start with a basic TSH test. Abnormal TSH, free T4, or free T3 levels can signal an underlying thyroid condition that requires further evaluation and treatment. Regular checkups help monitor your thyroid health over time.
Conclusion
Thyroid scans are important tools for checking how well your thyroid gland is working. They help doctors find and manage thyroid problems better. If you think something might be wrong with your thyroid, you should definitely chat with your doctor. They can guide you on whether a thyroid scan is right for you. Remember, this little gland in your neck has a big job in keeping your body healthy and functioning well! Take care of it!
References
- https://www.qldxray.com.au/services/nuclear-medicine/thyroid-scan
- https://www.racgp.org.au/afp/2012/august/thyroid-scans
- https://www.insideradiology.com.au/nuclear-medicine-thyroid-scan/