SPECT imaging helps doctors check your organs’ health. It might sound complex, but it’s a simple way to make sure your body’s running smoothly. Learn more!
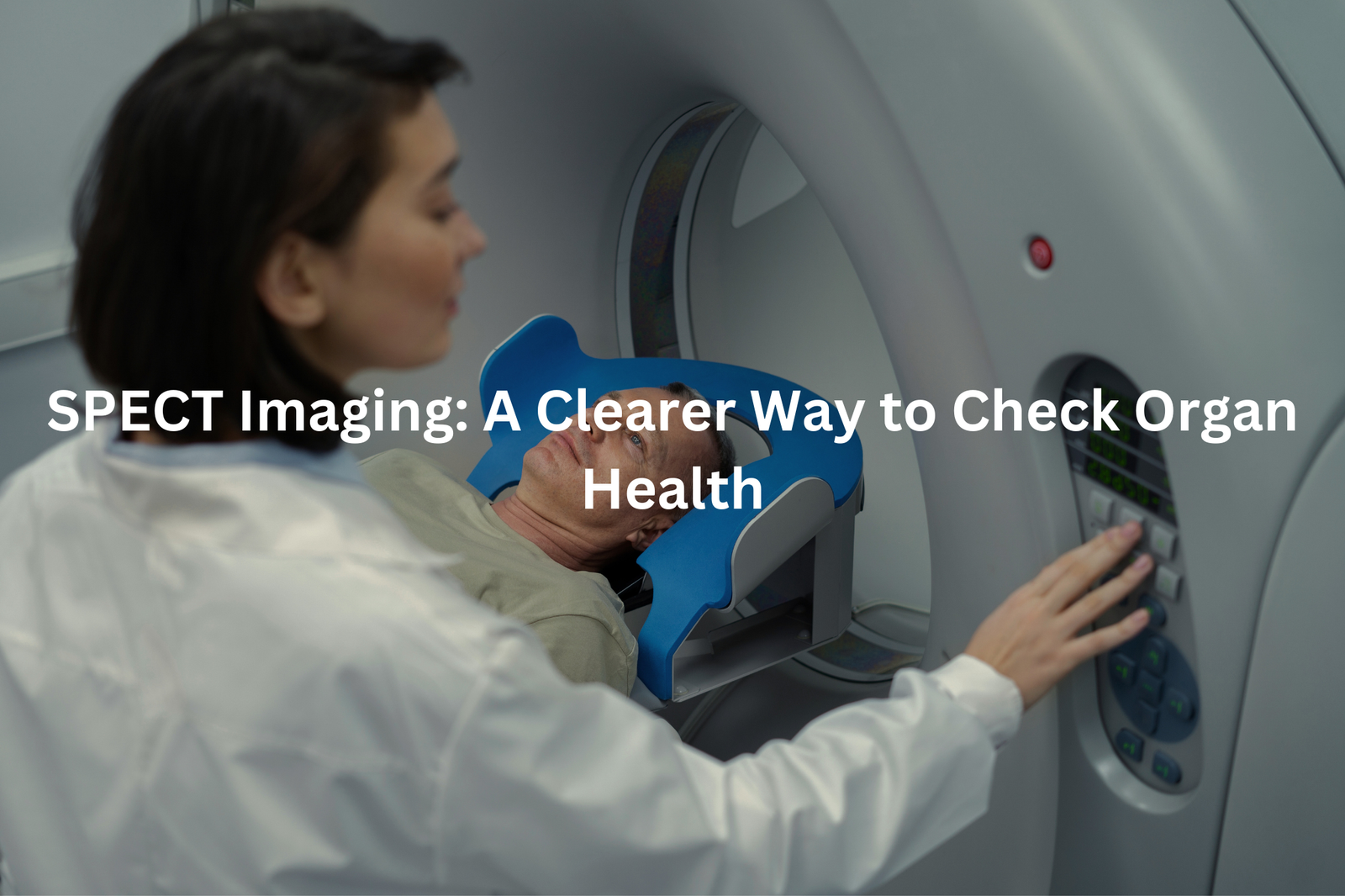
SPECT imaging is a special medical tool that lets doctors see how our organs are doing. It stands for Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography. With this high-tech method, doctors can capture pictures of our insides to check for problems, like heart issues or cancer. They use a small amount of radioactive material which highlights the organs on a scan.
This helps them spot any areas that might not be working properly. It’s pretty amazing how technology can help us stay healthy! If you’re curious about how SPECT imaging can benefit you or a loved one, keep reading!
Key Takeaway
- SPECT imaging uses special cameras to show how organs are functioning.
- It is non-invasive, meaning it doesn’t require surgery.
- SPECT can help doctors find problems early before we feel sick.
What is SPECT Imaging?
SPECT scans create detailed images of organs using a small amount of radioactive material (radiopharmaceutical). The process starts when a healthcare provider injects this tracer into a patient’s arm through an intravenous line.
As the tracer moves through the bloodstream, it reaches the target organ. A gamma camera rotates around the body, capturing the radiation signals from different angles. The computer then processes these signals into three-dimensional pictures.
The scanning process includes:
- Patient lying still on a table
- Camera rotating for 15-20 minutes
- Computer processing the data
The amount of radiation used in SPECT scans stays within safe levels, similar to what someone might get from a regular X-ray. The procedure doesn’t cause pain, and most patients can return to normal activities right after.
The images help doctors check how well organs function, spot potential problems, and plan treatments. This medical imaging technique proves particularly useful for examining the heart, brain, and bones.
How Does SPECT Work?
Nuclear medicine scans create detailed pictures of what happens inside the body. The process works through several key steps that help doctors see how organs function.
First, medical staff inject a small amount of radioactive material (called a tracer) into the patient’s vein(1). This tracer moves through the bloodstream and collects in specific organs or tissues. A special camera then takes pictures of areas where the tracer gathers.
The gamma camera rotates slowly around the patient, capturing multiple images from different angles. A computer combines these images to build a complete picture of the organ being studied. The final scan shows both the structure and function of organs like the heart, brain, or lungs.
These scans help doctors check:
- Blood flow patterns
- Organ function
- Tissue health
- Disease presence
The procedure takes about 30-90 minutes, depending on the type of scan needed. Patients can return to normal activities straight after the scan.
Common Uses of SPECT Imaging
SPECT imaging works as a powerful diagnostic tool in modern medicine. This advanced technology creates detailed 3D pictures of organs and tissues, helping medical professionals detect health issues without invasive procedures.
The process involves injecting a small amount of safe radioactive material (called a tracer) into the patient’s bloodstream. Special cameras then track this material as it moves through the body, creating clear images of different body parts.
Medical teams use SPECT imaging for several purposes:
- Brain scans to identify dementia or stroke damage
- Heart checks to examine blood flow patterns
- Bone scans to detect fractures or infections
- Lung imaging to assess breathing function
The procedure takes about 20 minutes to complete. Patients lie still on a table while the camera rotates around them, capturing images from multiple angles. The radiation exposure is minimal, similar to what someone might receive during a regular X-ray. This technology helps doctors spot potential health issues early, leading to more effective treatment plans.
Benefits of SPECT Imaging
Sources: ANSTO.
SPECT imaging serves as a vital diagnostic tool in modern medicine. This advanced scanning technique reveals crucial information about organ function, going beyond standard imaging methods.
The process works by tracking radioactive tracers through the body (typically injected via a small needle), creating detailed maps of organ activity. In cardiac cases, SPECT shows blood flow patterns in the heart muscle, while brain scans can detect areas with reduced circulation.
Key benefits of SPECT include(2):
• Shows real-time organ function
• Detects problems before symptoms appear
• Requires no surgical procedures
• Takes about 20-30 minutes to complete
The scan produces 3D images that help doctors spot issues like blocked arteries or decreased brain activity. Unlike traditional X-rays that only show structure, SPECT reveals how organs actually work. Patients need minimal preparation – just lying still during the scan while special cameras rotate around them.
Medical professionals consider SPECT particularly useful for heart disease, brain disorders, and certain types of cancer detection.
Safety of SPECT Imaging

The tiny amount of radioactive material used in SPECT imaging causes less radiation exposure than two chest X-rays. While some patients feel uneasy about the word “radioactive,” medical professionals follow strict safety protocols that make this procedure quite safe.
The radiation dose from SPECT scans measures about 6.3 millisieverts (a measurement unit for radiation exposure), which is less than the average person gets from natural background radiation in a year (around 3.1 millisieverts).
Medical staff take extra precautions for certain groups:
- Pregnant women might need to postpone scans
- Children receive adjusted doses based on weight
- Patients with allergies get special screening
Patients should discuss any worries with their healthcare provider, who can explain the process in detail. The benefits of early detection through SPECT scans often outweigh the minimal risks from radiation exposure. Most hospitals provide information sheets that break down the safety measures in simple terms.
Advances in SPECT Technology
SPECT imaging technology shows remarkable progress in medical diagnostics(3). The latest developments bring sharper images and faster scan times (typically 15-30 minutes per session), making the process more efficient for patients and medical staff.
Modern gamma cameras deliver higher resolution images with improved crystal detectors, helping doctors identify health issues with greater accuracy. The integration of SPECT with CT scanners creates hybrid machines that combine functional and anatomical imaging in one session.
Recent advances in radiopharmaceuticals contribute to enhanced image quality. These materials, carefully measured in millicuries (mCi), provide detailed views of organ function while maintaining safety standards set by Australian radiation guidelines.
The technology continues to advance in Australian hospitals, where dual-modality SPECT/CT systems show both organ function and structure. Medical teams can now detect issues earlier and plan treatments with more precision, a significant step forward in patient care.
These improvements in SPECT imaging mean better diagnostic results for patients across Australia.
FAQ
What is SPECT imaging and how does it work?
SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) is a medical imaging technique that uses small amounts of radioactive material and a special camera to create 3D images. It helps doctors see how organs and tissues are functioning. SPECT is commonly used to examine the heart, brain, and lungs.
How does SPECT differ from a CT scan or X-ray?
Unlike CT scans and X-rays, which show anatomical structures, SPECT scans use a radioactive tracer injected into the body. This tracer emits gamma rays, which are detected to create detailed images of blood flow and metabolism.
What are the benefits of SPECT lung imaging?
SPECT lung imaging helps diagnose lung diseases, such as pulmonary embolism, lung cancer, and COPD. It can measure lung function, perfusion, and ventilation.
How accurate is SPECT imaging?
SPECT is accurate for diagnosing heart, brain, and lung conditions. Hybrid imaging, which combines SPECT with other techniques, can improve results.
What are the potential risks?
SPECT uses low levels of radiation, which are generally safe. However, there is a slight risk of an allergic reaction to the radiotracer.
Conclusion
SPECT imaging is a neat way for doctors to see how our organs are working. They use a small amount of a radioactive tracer to take pictures that help identify problems early on. With its many uses and advantages, SPECT imaging becomes an important tool in medicine. If you ever need a SPECT scan, just remember it’s a simple and safe method for doctors to help you stay healthy!
References
- https://researchoutput.csu.edu.au/files/266782642/8799960_Published_article.pdf
- https://driainduncan.com.au/spect-ct/
- https://www.ansto.gov.au/safeguarding-future-of-australias-nuclear-medicine