This article explores CT scans, their uses, risks, and how they work for better health decisions.
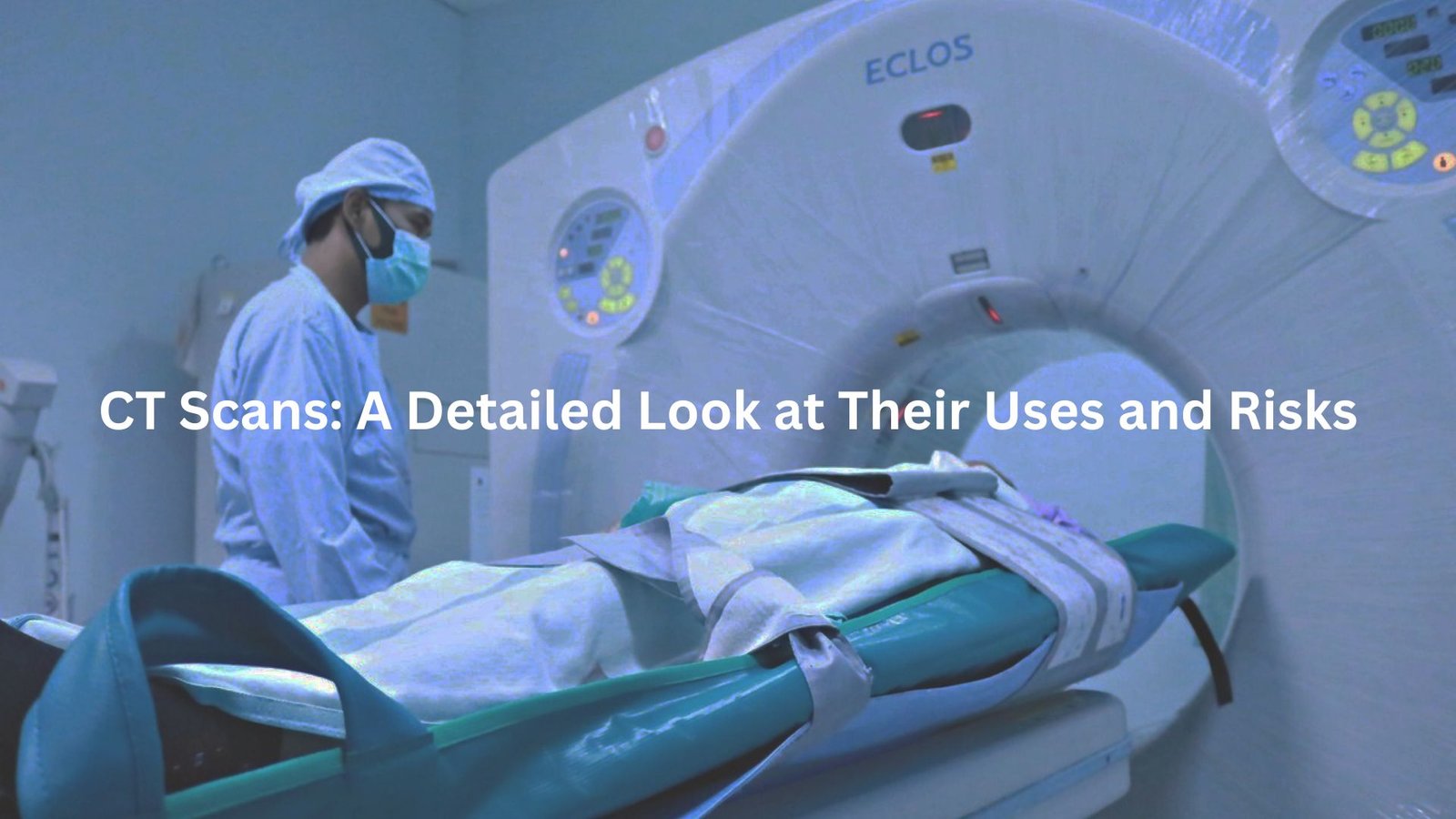
CT scans, short for computed tomography scans, play a crucial role in helping doctors peek inside our bodies. When someone feels unwell or suffers an injury, these scans become a key tool in diagnosing the problem. By using a special type of X-ray technology, CT machines capture multiple images, creating detailed pictures of internal organs and tissues.
This technology might seem complex, but it’s all about providing clarity in confusing moments. So, if you’re curious about how these scans really work, their various uses, and even the potential risks, keep reading! There’s plenty more to discover.
Key Takeaway
- CT scans are used for examining many areas of the body.
- There are risks related to radiation exposure from CT scans.
- Preparing for a CT scan is important for getting accurate results.
CT Scan Uses
CT scans are invaluable tools in the medical field, providing doctors with a window into the human body. With these scans, they can obtain detailed images of internal structures, revealing soft tissues, bones, and blood vessels. For instance, if someone experiences intense abdominal pain, a doctor may suggest an abdominal CT scan to uncover the root of the issue.
These scans don’t just offer snapshots of injuries; they play a critical role in cancer treatment as well. Doctors rely on CT scans to monitor Tumours, seeing whether they grow or shrink over time. This information is vital for crafting the most effective treatment plans.
Key uses of CT scans:
- Diagnosing conditions: They help identify diseases or injuries.
- Monitoring cancer: They show tumour size and location, guiding treatment.
- Planning procedures: Detailed images aid in preparing for surgeries.
In essence, CT scans are like the superheroes of diagnostics, empowering doctors to save lives with their insights.
CT Scans for Cancer
Credits: 7NEWS Australia
CT scans are essential in the fight against cancer, offering a crucial advantage in early detection. With their ability to reveal bone tumours and various types of cancers, these scans take cross-sectional images, like slicing through the body in thin layers. This unique approach provides doctors with a clearer view of any tumours that might be hidden within.
For instance, if a doctor suspects someone has lung cancer, they might recommend a CT scan of the chest. This scan becomes a key to uncovering any tumours nestled in the lungs, aiding in the timely diagnosis.
Important points about CT scans in cancer detection:
- Early discovery: CT scans help find cancer when it’s most treatable.
- Clear imagery: Cross-sectional slices provide detailed views of tumours.
- Informed decisions: The results guide doctors in planning the next steps.
In essence, these scans become vital allies for both doctors and patients in addressing cancer effectively. (1)
Abdominal CT Scan
An abdominal CT scan zooms in on the belly area, becoming a vital tool for doctors when they suspect something might be wrong. This test can reveal issues with important organs like the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. If someone experiences sharp stomach pains, their doctor might recommend this scan to get to the bottom of the problem.
The procedure is simple and quick. Patients lie on a narrow table as the CT machine glides around them, capturing detailed images of the internal organs. It usually takes just a few minutes, and wearing a hospital gown can help make the images clearer.
Key benefits of an abdominal CT scan:
- Detection of problems: Helps identify blood clots or inflammation.
- Diagnosing conditions: Can confirm appendicitis, which can cause severe illness.
- Quick process: Takes only a few minutes to complete.
In essence, this scan acts like a guide, leading doctors toward the right diagnosis and treatment for their patients.
Head CT Scan
A head CT scan is a specialised tool, focusing on the intricate details of the brain and skull. This scan becomes a crucial resource for doctors when they need to investigate potential issues like bleeding or tumours. For someone suffering from a severe headache, a doctor might recommend a head CT scan to rule out any serious conditions.
During the scan, the CT machine captures detailed images of the head, allowing doctors to determine if everything is functioning normally or if there are underlying problems. Sometimes, a contrast CT scan may be used, where a special dye is injected to highlight specific areas, making the images even clearer.
Key points about head CT scans:
- Detecting issues: Identifies bleeding or tumours in the brain.
- Assessing headaches: Helps ensure serious concerns are addressed promptly.
- Enhanced imaging: Contrast dye can improve visibility of certain areas.
In summary, these scans play a pivotal role in safeguarding our brain health, offering peace of mind when it’s needed most. (2)
Full-Body CT Scan
A full-body CT scan is a remarkable tool that provides a comprehensive view of the entire body. This scan is particularly useful for detecting cancers or other diseases that might be lying undetected. By taking numerous images from various angles, it creates a detailed 3D representation of the body, almost like a superhero X-ray.
Doctors often recommend full-body scans for patients considered at high risk for cancer. These scans allow physicians to examine all organs and tissues, looking for any signs of illness or abnormalities.
Key insights about full-body CT scans:
- Comprehensive detection: Useful for uncovering hidden cancers or diseases.
- Detailed imaging: Creates a 3D view of the whole body, offering clarity.
- Risk consideration: Important to be aware of radiation exposure, so not always the first option.
While these scans can be lifesaving, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits against the risks before proceeding, ensuring they are truly necessary.
How CT Scans Work
CT scans rely on a remarkable X-ray machine that spins around the body, capturing a series of images to provide an in-depth look at the inside. As it whirls, the machine shoots X-ray beams from a tube, creating slices of the body. Once these slices are taken, they are sent to a computer, which assembles them into detailed images, almost like piecing together a jigsaw puzzle.
Equipped with electronic X-ray detectors, this technology ensures that no detail goes unnoticed. The end result is a powerful image that reveals much more than a standard X-ray could.
Key features of CT scans:
- Detailed imaging: CT scans show intricate internal structures.
- Slice approach: Capturing images in slices allows for comprehensive analysis.
- Enhanced decision-making: Better clarity helps doctors make informed treatment choices.
With this advanced technology, CT scans become essential tools in medical imaging, helping healthcare professionals provide the best possible care for their patients.
Contrast CT Scans
Contrast CT scans offer a powerful advantage in medical imaging by using a special dye that enhances visibility of certain areas within the body. This dye can be administered through an IV or sometimes even taken as a drink, helping to spotlight blood vessels or organs and making it easier for doctors to identify any underlying issues.
For instance, if a doctor suspects a pulmonary embolism—essentially a blockage in the lungs—a contrast CT scan becomes a vital tool. The dye accentuates the blood vessels in the images, allowing the doctor to spot any potential clots more clearly.
Key points about contrast CT scans:
- Enhanced visibility: Dye highlights specific areas for improved analysis.
- Application: Useful in identifying conditions like pulmonary embolism.
- Allergy awareness: Important to discuss any allergies to dyes with your healthcare provider.
While these scans can provide crucial insights, it’s essential for patients to communicate openly about any concerns before the test. This ensures a safe and effective imaging experience.
Risks of CT Scans
CT scans can be incredibly useful for diagnosing various health issues, but it’s essential to be aware of the risks involved. One of the main concerns is radiation exposure. The X-ray machine relies on radiation to take its detailed pictures, and too much can potentially be harmful over time.
Repeated scans may increase a person’s lifetime risk of developing cancer. It’s a good idea for patients to talk openly with their doctors about the need for a scan. They should also consider safer options, like MRI scans, which don’t involve radiation.
Key considerations regarding CT scans:
- Radiation risks: Discuss the potential risks of exposure with your doctor.
- Alternative options: Explore safer imaging choices like MRI if possible.
- Allergic reactions: Although rare, be sure to inform your doctor of any allergies or health concerns.
By taking these precautions, patients can ensure they are making informed decisions about their health.
Preparing for CT
Getting ready for a CT scan is straightforward, but it’s crucial to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare team. Often, patients are required to fast for several hours before the scan. This means avoiding any food or drink during that time, which helps ensure the images come out as clear as possible.
Typically, healthcare providers will explain what needs to be done ahead of time. When it comes to clothing, wearing something comfortable is ideal, as you may need to change into a hospital gown for the scan.
If you’re scheduled for a contrast CT scan, staying hydrated is vital. Drinking plenty of water before the test can help with this process, especially as hydration can greatly enhance the effectiveness of the contrast dye.
Preparation tips for a CT scan:
- Fasting: Expect to fast for a few hours beforehand.
- Comfortable clothing: Wear something easy to remove.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water, especially for contrast scans.
By preparing well, patients can help ensure their scans go smoothly and effectively. (3)
Interpreting CT Results
After a CT scan, a radiologist— a doctor trained to read imaging results— examines the pictures. The radiologist writes a report on what they find and sends it to your doctor. Your doctor will then explain the next steps to you.
During your follow-up appointment, your doctor will break down the results. Sometimes, everything looks normal, showing typical body functions. Other times, they may discover something that requires further investigation or treatment.
Key points to consider post-scan:
- Radiologist’s role: This expert analyses the images and prepares a detailed report.
- Follow-up communication: Your doctor will explain the findings in understandable terms.
- Ask questions: If something isn’t clear, don’t hesitate to inquire. Understanding your health is crucial.
Feeling informed about your results can ease anxiety and empower you to make informed health choices, turning confusion into clarity.
Conclusion
CT scans are important tools in medical imaging. They help doctors look inside the body for diagnosis and treatment. While CT scans do involve some risks, especially from radiation, proper preparation can reduce these risks. Understanding the results is also key to staying informed about your health.
It’s always important for patients to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. Open communication helps people be well-prepared and informed about their health. It gives them the power to make the best choices for their journey.
FAQ
What is a CT scan?
A CT scan, also known as a computerised tomography scan, is a type of medical imaging that provides detailed pictures of the inside of the body. It helps doctors diagnose and monitor various conditions by creating 3-D images of organs and structures.
How does a CT scan work?
A CT scan uses special X-ray equipment to take many pictures of the body from different angles. A computer then combines these pictures to create detailed cross-sectional images, which show the inside of the body in a way that is clearer than a regular X-ray.
Are CT scans safe?
CT scans are generally safe, but they do use a small amount of radiation. While the risk from radiation is low, it’s important to talk to your doctor about the need for the scan and whether there are any alternative imaging exams that might be better suited for you.
Do CT scans hurt?
No, a CT scan is a painless procedure. You may be asked to lie still for a few minutes while the scan takes place, and in some cases, a special dye called contrast may be used to help highlight certain areas inside your body. Some people may feel a slight discomfort from the injection of contrast, but it is usually quick and mild.
How long does a CT scan take?
A typical CT scan usually takes only a few minutes. However, you may need to spend extra time getting ready, depending on the type of scan. The appointment time can vary depending on the area being scanned and whether you need contrast.
Can I eat or drink before a CT scan?
Your doctor will give you specific instructions about whether you need to avoid food or drinks before your CT scan. In some cases, you may need to fast for a few hours beforehand, especially if you’re having a scan with contrast.
Are there any risks with CT scans?
The main risk of a CT scan is the exposure to radiation. While the amount of radiation used is generally low and safe for most people, it can pose a risk, especially for pregnant women and children. Always talk to your doctor if you are concerned about the effects of radiation exposure.
What happens after a CT scan?
After the scan, you can usually go about your day as normal. If you had contrast used during the procedure, your doctor may ask you to drink extra fluids to help remove it from your body. The results of your scan will be sent to your doctor, who will discuss the findings with you.
Can CT scans detect cancer?
Yes, CT scans can be used to detect signs of cancer, such as Tumours or abnormal growths in the body. However, they are not used as the only method to diagnose cancer. Your doctor may recommend other tests to confirm any findings from the scan.
Can children have CT scans?
Yes, children can have CT scans, but extra care is taken to reduce their exposure to radiation. Doctors will make sure the scan is necessary and will use the lowest possible dose of radiation. For children who are anxious, some may be given the option of having the scan without sedation.
References
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/ct-scan
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/ct-scan
- https://www.cancer.org.au/ct-scan